Calculate the Length of the Continuous Footing
Need more? Ask Us a Question
This module provides analysis of a unit strip of a continuous wall footing with applied axial, moment and shear loads. Overburden loads can also be specified, and will apply to the surface area of the footing (except the area covered by the wall). The module also provides automatic calculation of allowable soil bearing pressure increases based on footing width and/or depth below surface.
The module checks service load soil pressure, overturning stability, sliding stability, uplift stability, footing flexure and one-way footing shear.

General
This tab collects material property values, strength reduction factors, and other settings that influence the design.
f'c
28-day compressive strength of the concrete.
fy
Yield point stress of reinforcing.
Ec
Modulus of elasticity of concrete.
Concrete Density
The density of the concrete is used to calculate the self weight of the footing when the option is selected.
Phi Values
Enter the capacity reduction values to be applied to Vn and Mn.
Include footing weight as dead load
Click [ Yes ] to have the module calculate the weight of the footing and apply it as a downward load. The footing self weight will be multiplied by the dead load factor in each load combination.
Min Steel Ratio - Temperature/Shrinkage Reinf.
Enter the minimum ratio for temperature/shrinkage steel, calculated using the footing thickness. This will trigger a warning message if the section is under-reinforced.
Minimum Overturning Safety Factor
Enter the minimum allowable ratio of resisting moment to overturning moment. If the actual ratio is less than the specified minimum ratio, it will trigger a message that overturning stability is not satisfied.
Minimum Sliding Safety Factor
Enter the minimum allowable ratio of resisting force to sliding force. If the actual ratio is less than the specified minimum ratio, it will trigger a message that sliding stability is not satisfied.

Soil Allowables
Allowable Soil Bearing Pressure
Enter the allowable soil bearing pressure. This is a service load resistance and will be compared to calculated service load soil pressures (loads not factored as in strength design).
Increase Bearing by Footing Weight
Click [ Yes ] to tell the module to calculate the weight of one square foot (plan view) of footing and add it to the allowable soil bearing value. This has the effect of not penalizing the soil for the self weight of the footing, and is useful for situations where the geotechnical engineering report provides allowable net bearing pressures.
Soil Passive Sliding Resistance
Enter the value of passive soil pressure resistance to sliding. This value will be used to determine a component of sliding resistance that is generated by the passive pressure of the soil. The sliding resistance due to passive pressure is then added to the sliding resistance due to friction to determine the total resistance to sliding for each load combination.
Coefficient of Soil/Concrete Friction
Enter the coefficient of friction between soil and footing to use in sliding resistance calculations.
Soil Bearing Increase
This section allows you to specify some dimensions that, when exceeded, will automatically increase the allowable soil bearing pressure.
Footing base depth below soil surface : The distance from the bottom of the footing to the top of the soil. This value is used to determine allowable soil bearing pressure increases and soil passive sliding resistance, but it is NOT used in any other calculations in this module.
Increases based on footing depth : Provides a method to automatically apply increases to the basic allowable soil bearing pressure based on footing depth below some reference depth. Collects the following parameters:
Allowable pressure increase per foot : Specifies the amount that the basic allowable soil bearing pressure can be increased for each foot of depth below some reference depth.
When base of footing is below : Specifies the required depth in order to start realizing incremental increases in the allowable soil bearing pressure on the basis of footing depth.
Example : Assume the following: Basic Allowable Soil Bearing Pressure = 3 ksf. Footing base is 6'-0" below soil surface. The Geotechnical report specifies that a 0.15 ksf increase in bearing pressure is allowed for each foot of depth when the base is deeper than 4' below top of soil. Since you've indicated that the footing is 6' below the soil surface, the module will automatically calculate the adjusted allowable soil bearing pressure to be 3 ksf + (6' - 4') * 0.15 ksf = 3.30 ksf.
Increases based on footing width : Provides a method to automatically apply increases to the basic allowable soil bearing pressure based on footing width greater than some reference dimension. Collects the following parameters:
Allowable pressure increase per foot : Specifies the amount that the basic allowable soil bearing pressure can be increased for each foot of width greater than some reference dimension.
When maximum length or width is greater than : Specifies the required dimension in order to start realizing incremental increases in the allowable soil bearing pressure on the basis of footing width.
Example : Assume the following: Basic Allowable Soil Bearing Pressure = 3 ksf. Footing measures 6'-0" wide. The Geotechnical report specifies that a 0.15 ksf increase in soil bearing pressure is allowed for each foot when the width of the footing is greater than 4'-0". The module will automatically calculate the adjusted allowable soil bearing pressure to be 3 ksf + (6' - 4') * 0.15 ksf = 3.3 ksf.
Note: Increases based on footing depth and width are cumulative.

Footing Size & Reinforcing
Dimensions tab
Footing Width: Define the width of the footing.
Wall Width: Define the width of the supported wall.
Wall center offset from footing centerline: Define the dimension between the centerline of the wall and the centerline of the footing. Positive offsets shift the wall toward the right edge of the footing.
Footing Thickness: Define the thickness of the footing.
Auto Calculate Footing Size & Thickness: Provides an automated routine to increase footing dimensions until soil pressures are satisfied and one-way shear is acceptable.
Note: Any applied overburden loads will be omitted from the area occupied by the wall.

Reinforcing tab
Reinforcing Bar Size: Indicate the rebar size to consider for the bars that run parallel to the footing width.
Reb ar Spacing: Provides an option to either specify an explicit value for the rebar spacing, or to specify the number of bars in a 12-inch length.
Rebar Center to Concrete Edge @ Bottom: Specify the clear cover plus 1/2 the diameter of the rebar.

Applied Loads
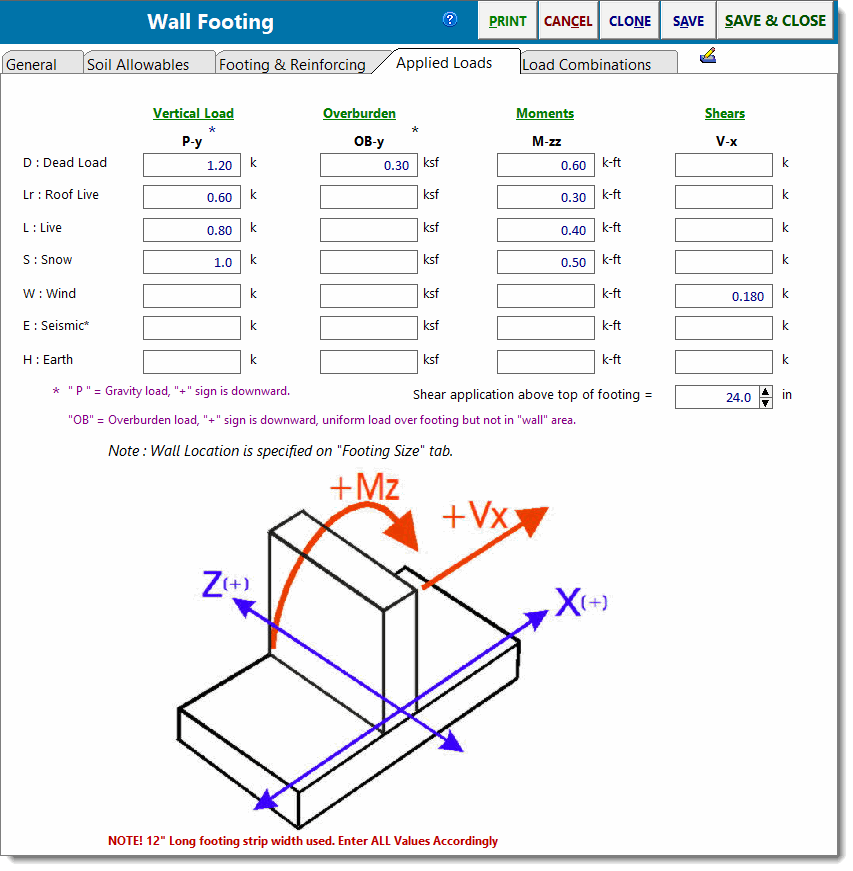
Vertical Loads tab
Provides input fields for vertical loads and overburden pressures. Vertical loads are specified in units of kips per foot, and they are considered to act at the center of the width of the wall. Overburden loads are specified in units of kips per square foot, and they are considered to act on the top surface area of the footing, excluding the area occupied by the wall.

Moments & Shears tab
Provides input fields for moments and shears. Moments are specified in units of foot kips per foot. Shears are specified in units of kips per foot, and they are considered to act at the height specified in the field named Shear application above top of footing . Shears will produce a moment equal to the shear force times the distance from the bottom of the footing to the location of application of the shear force.
Load Combinations
The Load Combinations tab is used to specify the load combinations to be used in the design. The LRFD Load Combinations tab controls the combinations that are used for reinforced concrete design checks. The Soil Pressure Combinations tab controls the combinations that are used for evaluating soil bearing pressure. A Soil Increase factor can be applied on a load combination by load combination basis, as permitted by the geotechnical engineering report. The Stability Combinations tab controls the load combinations that are used to perform the serviceability checks for Overturning, Sliding, and Uplift.
These tabs allow the user to select from load combination sets that are supplied with the program or to select from custom load combination sets that have been created and saved on the user's machine. It is also possible to unlock the selected load combination set and make edits to the factors directly in this view.
The user has control over which combinations are run and which are ignored. Finally, these tabs allow the user to specify whether the program should consider the algebraic sign of the specified load factors on wind loads and seismic loads to be reversible or not. This can be a convenient way to ensure that these loads are investigated as acting in both positive and negative directions, if that is the design intent. Note, however, that if selected, the algebraic sign reversal will be applied to ALL wind loads and/or ALL seismic loads including horizontally AND vertically applied loads.

Calculations
Results tab
This tab summarizes the controlling values (highest utilization ratio) for each design consideration, from all of the load combinations that have been run. For the controlling load combination, it presents the Applied load, the Capacity or available resisting load, the ratio of the Applied to the Capacity, and the governing load combination that produces this controlling ratio.

Soil Pressures tab
For each service load combination, this tab presents the total vertical load, the resultant eccentricity, the soil pressures on the left and the right ends of the footing, the allowable soil pressure, and the ratio of the actual to the allowable soil pressure.

Overturning & Sliding Stability tab
For each service load combination, this tab presents the overturning moment, the resisting moment and the ratio of the resisting to overturning moment about the left and right edges of the footing.

It also reports the sliding force, the resisting force, and the ratio of the resisting to sliding force.

Footing Bending tab
This tab reports the results of the flexural design on a load combination by load combination basis.

Footing Shear tab
This tab reports the results of the shear design on a load combination by load combination basis.

3D tab
This tab presents the 3D rendering of the footing :

2D tab
This tab presents plan and section views of the footing :

Source: https://enercalc.com/sel_help/wall_footing.htm
0 Response to "Calculate the Length of the Continuous Footing"
Post a Comment